Realica VR
Scientifically Proven Reduction for Anxiety and Pain
REALICA® VR, our advanced virtual reality technology designed for healthcare environments, represents a fundamental advancement in supporting patients during medical procedures. Developed in close collaboration with physicians and neuroscientists, this innovative solution incorporates principles derived from neurophysiology, mindfulness, psychology, clinical hypnotherapy, and breathing techniques.
Several clinical studies [1] have scientifically confirmed that immersive experiences in virtual worlds through REALICA® VR can significantly reduce both pain and anxiety in patients. In particular, a significant percentage, ranging from 60% to 80% [2], experiences acute anxiety during medical procedures, and REALICA® VR emerges as an effective solution to mitigate this discomfort.
Results from specific studies [1] indicate that the use of VR treatment pre and postoperatively can reduce the need for anesthesia, decrease postoperative pain, reduce analgesia requirements, and overall improve the quality of recovery. These findings are supported by authoritative publications emphasizing the effectiveness of virtual reality in reducing pain and anxiety in various medical contexts.
Notes to Citations
1. “The effectiveness of virtual reality on reducing pain and anxiety in burn injury patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials” – Ahmadpour N, Randall H, Choksi H, Gao A, Vaughan C, Poronnik P. – Pubblicato su Burns & Trauma. 2020.
“The effectiveness of virtual reality distraction for reducing pain: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials” – Malloy KM, Milling LS. – Pubblicato su Journal of Pain. 2010.
“Virtual reality for the induction of anesthesia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials” – Chan A, Chung A, Paoli A, Ho S, Yu B. – Pubblicato su Journal of Clinical Anesthesia. 2021.
2. “A survey of 800 patients’ knowledge, attitudes, and concerns regarding anesthesia” – K Shevde, G Panagopoulos.
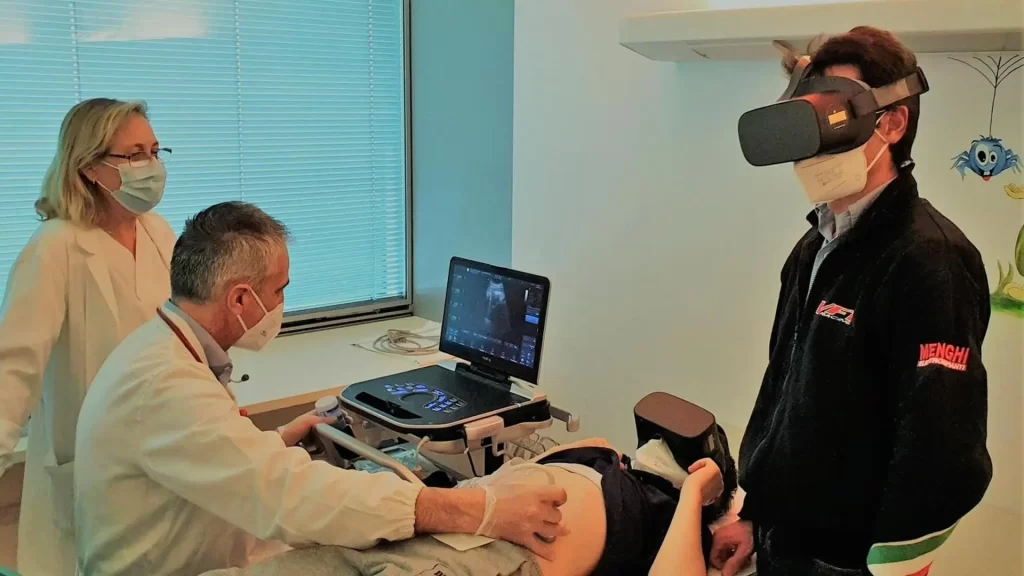
HOW IT WORKS?
Virtual and Digital Sedation: The Point in the Scientific Context
Virtual sedation, as a complement to traditional pharmacological sedation, has been the subject of in-depth studies and numerous international scientific publications in recent years.
While traditional sedation relies on the use of sedative drugs to induce a state of calm or drowsiness in patients, virtual sedation stands out for its use of virtual reality and immersive digital experiences.
This approach aims to enhance relaxation and reduce anxiety during medical procedures by inducing positive and relaxing experiences.
Some Relevant Scientific Publications
1. “Virtual sedation as a substitute for pharmacological sedation during PICC placement in pediatric patients: A feasibility study” – Sanna Gianuario, Camporesi Anna, Diotto Veronica, Abbiati Giacomo, Torri Adriano, Gemma Marco – A study exploring the application of virtual sedation during the placement of PICC in pediatric patients.
2. “Small surgeries, big smiles: using virtual reality to reduce the need for sedation or general anesthesia during minor surgical procedures” – Taylor JS, Chandler JM, Menendez M, Diyaolu M, Austin JR, Gibson ML, Portelli KI, Caruso TJ, Rodriguez S, Chao SD. – A study demonstrating the effectiveness of virtual reality in reducing the need for sedation or general anesthesia during minor surgical procedures.
3. “Is Virtual Reality Ready for Prime Time in the Medical Space? A Randomized Control Trial of Pediatric Virtual Reality for Acute Procedural Pain Management” – Gold JI, Mahrer NE. – A study evaluating the effectiveness of virtual reality in managing acute pain during pediatric procedures.
4. “Virtual Reality Interventions for Needle-Related Procedural Pain, Fear and Anxiety-A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis” – Czech O, Wrzeciono A, Rutkowska A, Guzik A, Kiper P, Rutkowski S. – A systematic review and meta-analysis of virtual reality applications in managing pain and anxiety related to needle procedures.
5. “Virtual reality interventions and the outcome measures of adult patients in acute care settings undergoing surgical procedures: An integrative review” – Wang S, Lim SH, Aloweni FBAB. – An integrative review of virtual reality applications in adults undergoing surgical procedures in acute care settings.
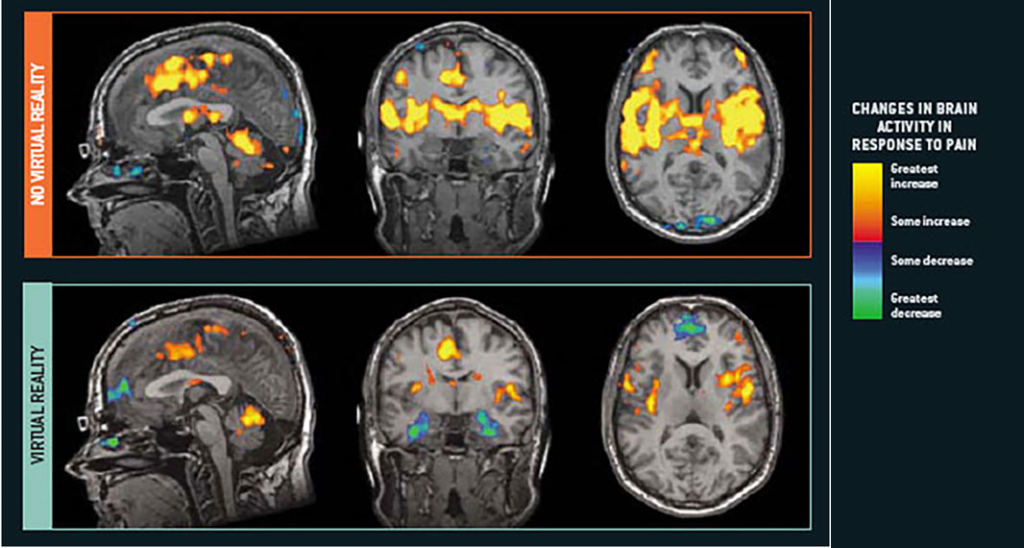
Virtual Reality as Pain Distraction
Images from an MRI scan clearly reveal the brain regions involved in pain perception and their changes during immersion in a virtual reality world. According to Dr. Sharar, cognitive distraction during painful experiences has the ability to divert attention from painful stimuli.
The patient’s full immersion in an engaging virtual world leads to a significant reduction in pain perception.
Image provided by Dr. Sam Sharar/University of Washington
Virtual reality influences the sensory and emotional dimensions of pain control. It also regulates brain activity in regions related to acceptance, resilience, and cognitive processing of pain. The reduction of activity in five specific brain areas related to pain highlights the potential impact of virtual reality in modulating the patient’s pain perception.
HOW IT WORKS
REALICA® VR is a ready-to-use solution.
No special attention is required other than wearing the mask correctly.


